The issue of maritime safety has always been an indispensable part of the shipping and merchant vessel industry. This is exemplified by the establishment of maritime treaties such as the IMO’s International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) and cross-national organizations such as the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA). Traditionally, maritime safety initiatives and practices aim to preserve the well-being of ships, their cargo, and the people onboard from dangers such as collisions, extreme weather conditions, hull stress, equipment malfunctions, and even piracy.
While this hasn’t changed, what has changed in recent years are the ways in which technological advancements can significantly enhance maritime safety. Like other sectors, AI adoption is gaining momentum in the shipping industry and is set to become a mainstream technology in the coming years. According to the ‘Global Maritime Trends 2050 Report‘, commercial ships will increasingly rely on machine learning, AI and satellite technology to improve shipping safety and efficiency by optimizing decision-making, and even addressing safety issues that may arise due to lack of situational awareness or data.
The connectivity backbone
The basis for the vast potential of innovation regarding maritime safety is connectivity. Maritime communication has evolved from Morse code and radio communication to phone communication and internet on board. Yet the current availability of satellite connectivity – especially Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites – and its integration with 5G cellular networks allows ships to share information with each other and with shore-based facilities with unprecedented real-time speed. This is important because digital ships generate vast amounts of key data that traditional connectivity infrastructure cannot deal with efficiently. Yet a shift from 4G to 5G cellular networks, for example, allows data transfers up to 100 times faster than before.
Technology innovations in the shipping industry enabled by robust satellite connectivity have the ability to enhance decision-making, optimize route planning, and provide alerts on navigational hazards, allowing ships to avoid dangers, mitigate risks, and proactively reduce maritime accidents.
Innovations redefining maritime safety standards
The maritime sector is experiencing significant technological advancements that are redefining its safety standards. Perhaps the most persistent safety problem remains ship collisions, which, mostly due to human error and poor visibility conditions, continue to negatively impact the industry in terms of fatalities, ship and cargo damage, environmental harm, costs, and stakeholder confidence. Yet the following technologies, collectively known as Maritime 4.0, form a solid foundation that is already reducing ship collisions worldwide, seen in an overall 33% reduction in close encounters in open waters and a 40% decline in crossing events. From optimized voyage technologies to AI-based navigation systems, digitalization in maritime is quickly turning the digital ship concept into a reality.
Internet of things (IoT) sensors:
Sensors on ships have been standard for decades, but IoT sensors are taking things to the next level. Unlike traditional sensors, IoT sensors are empowered by internet connectivity, allowing them to deliver real-time data to specific parties. These smart sensors are crucial for maritime safety, providing real-time insights into vessel integrity, environmental conditions, and potential navigational hazards. They enable proactive risk management by measuring parameters such as hull stress, temperature, machine operations, and weather conditions. With IoT sensors, crews on-board and on-shore teams can promptly detect structural weaknesses, monitor sea state changes, and address alerts that pinpoint potential risks in advance.
Predictive analytics:
Powered by AI and machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics are crucial for enhancing maritime safety and operational efficiency. These technologies analyze data from ship sensors and cameras to forecast adverse weather conditions, enabling preemptive measures. This proactive approach allows ship crews to optimize routes in real-time and navigate the most efficient ones, minimizing weather-related accidents while reducing fuel consumption, and supporting efforts in decarbonization. Additionally, predictive analytics predict potential system failures by identifying maintenance issues and ensuring equipment reliability. This proactive monitoring minimizes downtime, ensuring ships operate smoothly and safely, thereby enhancing overall maritime operations.
Remote monitoring systems:
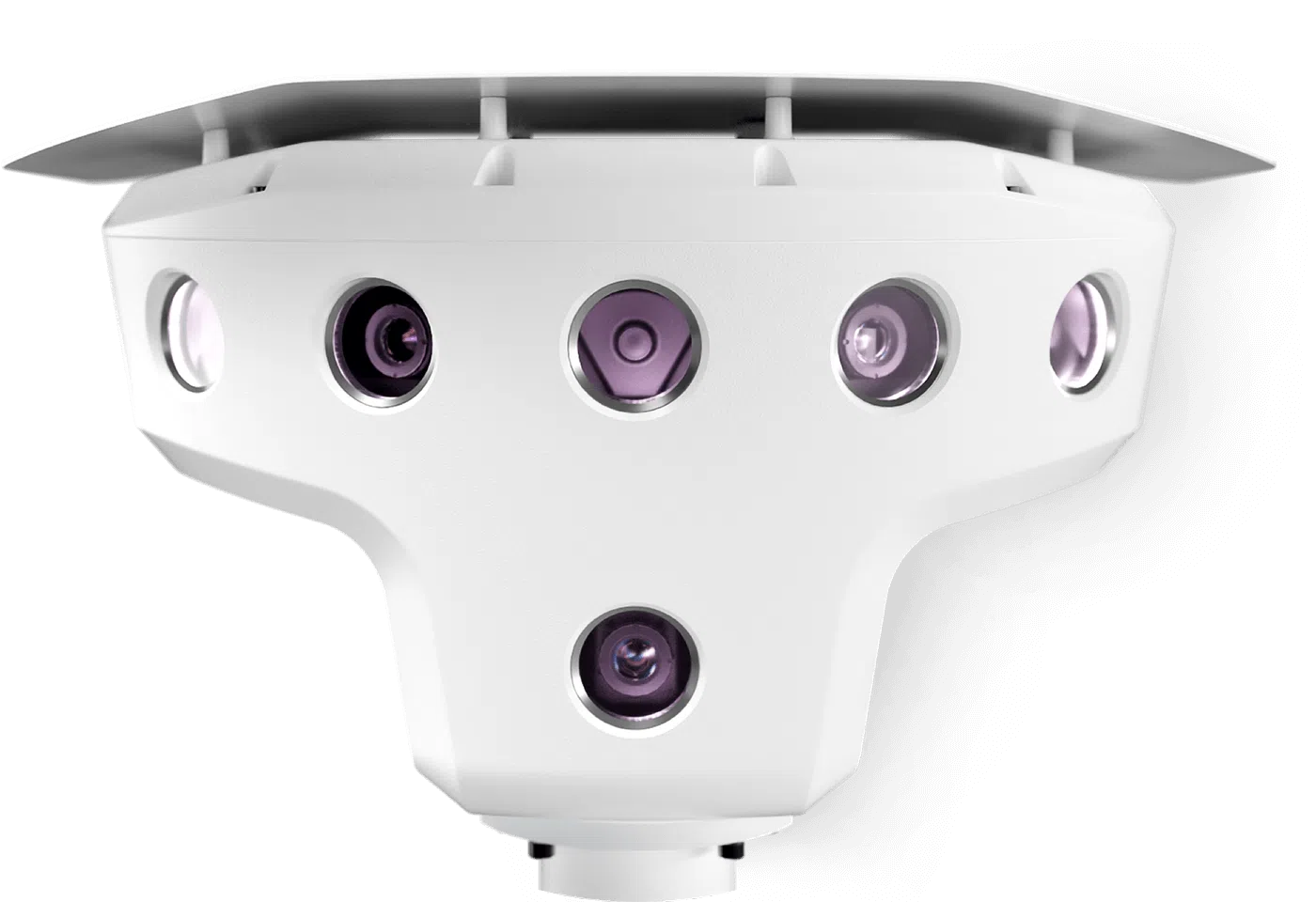
Remote monitoring technology significantly enhances operational efficiency and safety by offering a comprehensive overview of vessel performance, irrespective of location. This technology empowers operators onboard and in on-shore offices with complete visibility into vessel operations and navigation routes. It enables continuous monitoring of ship performance and allows for prompt intervention in case of anomalies. HD cameras play a critical role by capturing both internal operations and external surroundings, essential for maintaining safety and efficiency, particularly in challenging environments. Real-time data from these systems allow for proactive maintenance scheduling and optimized vessel performance, preventing safety incidents through early anomaly detection and timely intervention.
AI-based computer vision:
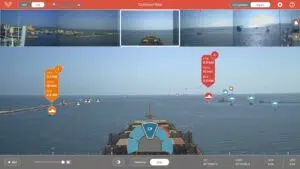
AI-based navigation systems leverage high-definition cameras powered by advanced algorithms to detect, classify, and analyze navigational hazards in real-time. These ship collision avoidance systems, exemplified by Orca AI’s SeaPod, act as additional watchkeepers, or bridge navigational watch alarm systems (BNWAS), significantly enhancing situational awareness for crews even in challenging conditions. They promptly identify obstacles like other vessels, floating debris, or small and distant objects that may not transmit AIS signals, enabling crews to adjust courses in advance. This proactive approach prevents the need for emergency maneuvers, ensuring operational safety while reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Continuous data processing makes these systems smarter by the day, ensuring reliability even in the most dynamic and congested traffic situations while surpassing traditional crew watchmen in accuracy.
Big data and data analytics:
Modern ships are hubs of information, gathering data from sensors, cameras, weather forecasts, crew communication, and ship-to-port interactions. Today’s empirical models process only about 10% of vessel data, compared with 90% for AI models, which can then generate accurate performance insights. Big data analytics solutions play a pivotal role in processing this influx of information from diverse sources. They enable the ship’s captain and crew to maintain a comprehensive view, highlighting critical insights in real-time while managing intricate details. This capability is essential for charting optimized voyages that prioritize safety, fuel efficiency, and decarbonization. Additionally, data analytics streamline the identification of crucial maintenance-related information amidst the vast data clutter, ensuring proactive ship maintenance strategies.
Autonomy on-board: Pioneering a new safety paradigm
This technological progress promises enhanced navigation precision and reliability while minimizing human error. With cutting-edge sensors, cameras, and AI systems already onboard modern ships, autonomous shipping emerges as a revolutionary concept in maritime operations, poised to redefine safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness through optimal connectivity and AI precision. Autonomous or semi-autonomous ships, requiring minimal crew involvement, aim to eliminate human error, ensuring safer voyages. With the potential to reduce maritime accidents by up to 90%, the autonomous ship revolution could mark a pivotal moment in maritime safety history.
However, the adoption of autonomous practices remains a gradual process within the highly traditional and heavily regulated maritime industry. It involves incrementally introducing autonomous systems and automation among ship crews, accompanied by rigorous testing and clear protocols to ensure their reliability. Despite these challenges, embracing these innovations offers a pathway toward a safer and more efficient maritime future, where autonomous technologies play a pivotal role in transforming industry practices for the better.